C++字符串和vector
C++的字符串是一个对象,存在于std标准库中,是std标准库提供的自定义类类型
所占存储空间较大,40字节,数据成员一般都包含

vector是一种动态数组,也存在与std标准库中,一般都有size和capacity两个数据成员
字符串创建方式
默认创建
C语言字符串创建
指定长度的单个字符创建
字符串拼接
只能用+拼接,+两边必须有一个是string类对象
string s4 = s3 + s2;
s4 = s3 + "Hello";
s4 = "Hello" + s3;
|
字符串追加
追加特定长度字符
追加字符串
追加string类对象
追加string类对象指定起始位置指定长度
字符串截断
//参数1,pos,指定起始位置,参数2,len,指定长度
cout<<s3.substr(0,3)<<endl;
|
auto
C++的一种自动遍历模式,auto是自动推导,如果不带引用可能会浪费空间
for(auto& t: s3)
{
cout<<t<<' ';
}
|
完整代码
#include <iostream>
using std::cout;
using std::endl;
using std::string;
void sp(string& s)
{
cout << "s:" << s << endl;
cout << "s:sizeof:" << sizeof(s) << endl;
cout << "s.size:" << s.size() << endl;
cout << "s.length:" << s.length() << endl;
cout << endl;
}
int main()
{
string s1;
string s2("Hello");
string s3(10, 'a');
sp(s1);
sp(s2);
sp(s3);
string s4 = s3 + s2;
s4 = s3 + "Hello";
s4 = "Hello" + s3;
sp(s4);
s3.append(3, 'a');
sp(s3);
s3.append("Hello");
s3.append(s2);
s3.append(s2,0,5);
sp(s3);
cout << s3.substr(0, 3) << endl;
cout << &s1 << endl;
cout << endl;
for (auto& t : s3)
{
cout << t << ' ';
}
return 0;
}
|
vector创建方式
默认创建
初始化创建
vector<int> numbers(10,0);
|
vector操作
添加元素
删除末尾元素
代码实现
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
using std::cout;
using std::endl;
using std::vector;
void vp(vector<int>& numbers)
{
cout << "numbers:size:" << numbers.size() << endl;
cout << "numbers.capacity:" << numbers.capacity() << endl;
}
int main()
{
vector<int> numbers;
vp(numbers);
for (int i = 0; i < 10; ++i)
{
numbers.push_back(i);
vp(numbers);
}
vector<int> a(11, 0);
for (auto& t : a) cout << t << ' ';
vp(a);
return 0;
}
|
有一个需要我们值得注意的地方
vector对象在size为capacity时且还需要再添加新的元素时,会进行扩容
扩容步骤
申请一个原先x倍的空间
将旧空间的元素拷贝到新空间中
销毁旧空间,vector数组指向新空间
不同编译器在扩容时的倍率不同
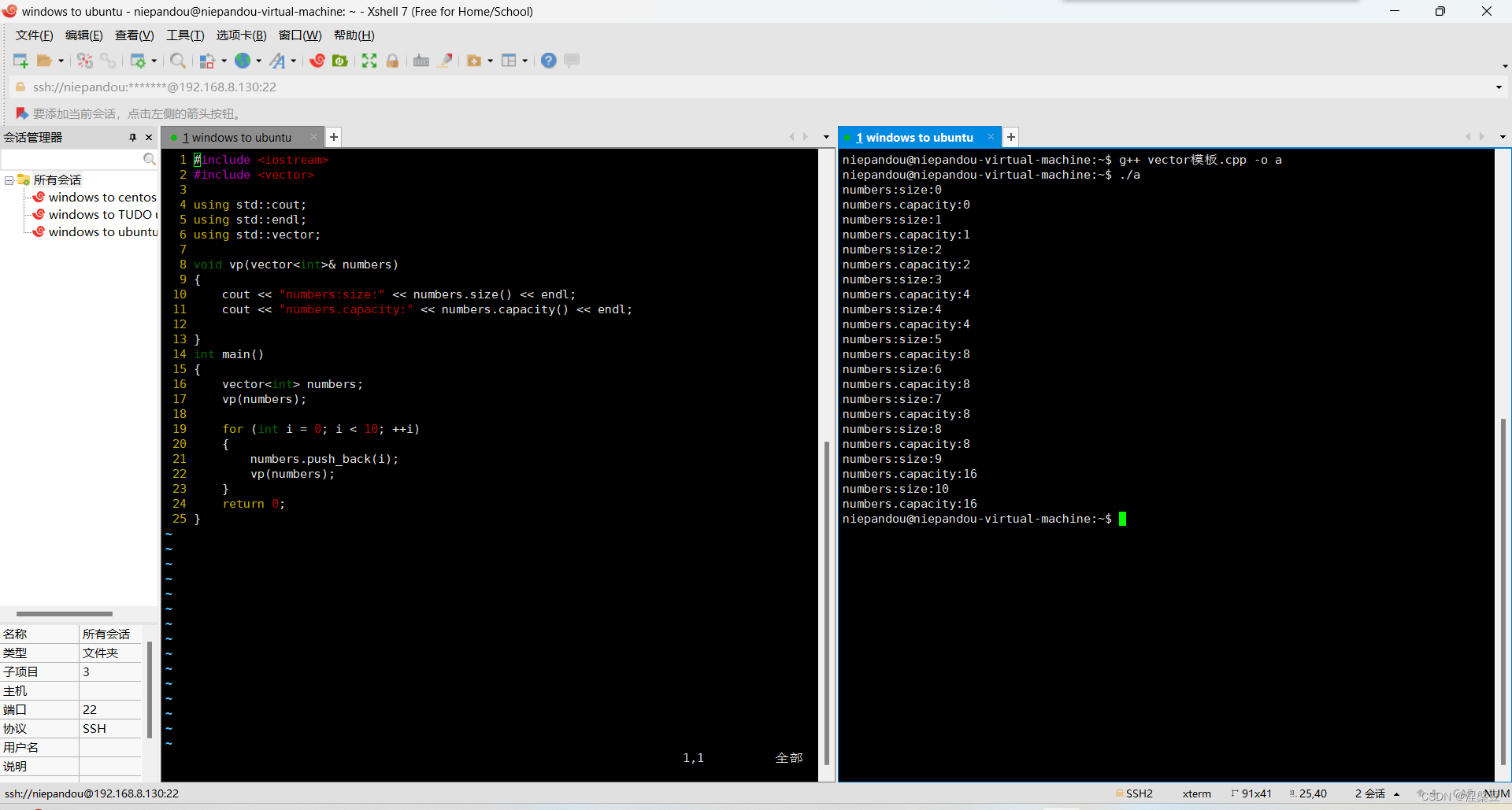
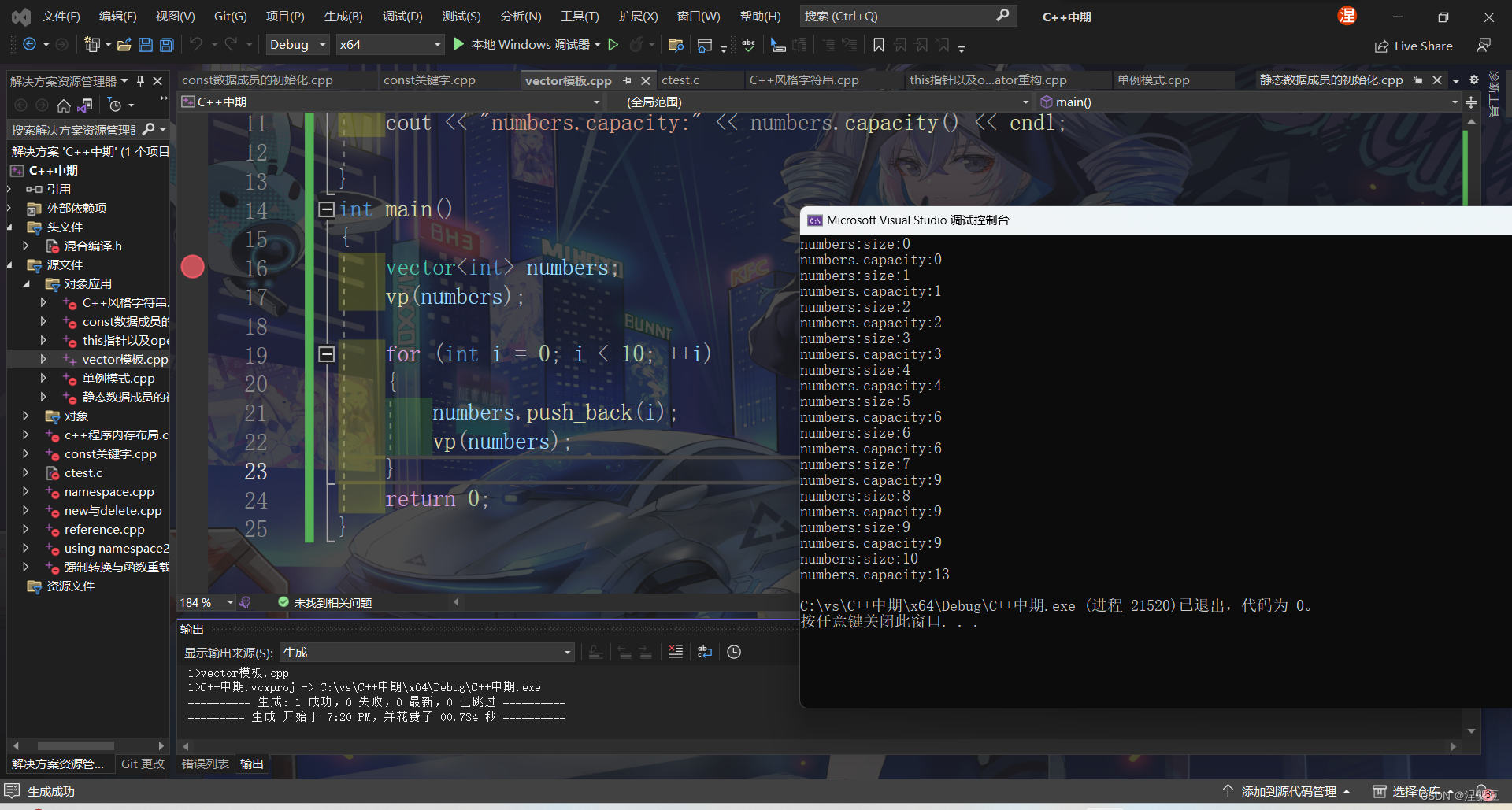
可以看到,一般的编译器扩容一般都是2倍扩容,而vs会以原来的1.5倍扩容
new与delete重构
new与delete的工作步骤
new:
1.调用operator new标准库函数申请未定义的空间
2.在该空间调用构造函数初始化对象
3.返回一个相应类型的指针
形式 void* operator new(size_t)
delete
调用析构函数
调用operator delete标准库函数回收对象空间
代码实现
#include <iostream>
#include <cstdlib>
#include <cstring>
using std::cout;
using std::endl;
class Student
{
public:
Student(const char* name,const int& id)
:_name(new char[strlen(name) + 1]())
,_id(id)
{
strcpy(_name,name);
cout<<"Have done create"<<endl;
}
void release()
{
delete[] _name;
_name = nullptr;
}
~Student()
{
if(_name) release();
cout<<"~Student"<<endl;
}
void print() const
{
cout << "name:" << _name << endl;
cout << "id:" << _id << endl;
}
void* operator new(size_t sz)
{
cout<<"Operator new"<<endl;
return malloc(sz);
}
void operator delete(void* p)
{
cout<<"Operator delete"<<endl;
free(p);
}
private:
char* _name;
int _id;
}
int main()
{
return 0;
}
|
size_t 类型无需担心会不会申请出错
new与delete重构应用
生成栈对象的条件
1.需要合法的构造函数
2.需要合法的析构函数
生成堆对象的条件
1.需要合法的operator new库函数
2.需要合法的构造函数
只能生成栈对象
方法:将 operator new库函数私有化
#include <iostream>
#include <cstdlib>
#include <cstring>
using std::cout;
using std::endl;
class Student
{
public:
Student(const char* name,const int& id)
:_name(new char[strlen(name) + 1]())
,_id(id)
{
strcpy(_name,name);
cout<<"Have done create"<<endl;
}
void release()
{
delete[] _name;
_name = nullptr;
}
~Student()
{
if(_name) release();
cout<<"~Student"<<endl;
}
void print() const
{
cout << "name:" << _name << endl;
cout << "id:" << _id << endl;
}
private:
char* _name;
int _id;
void* operator new(size_t sz){}
void operator delete(void* p){}
};
void test1()
{
Student s1("Rose",100);
s1.print();
}
int main()
{
test1();
return 0;
}
|
打印结果
Have done create
name:Rose
id:100
~Student
|
只能生成堆对象
方法:将析构函数私有化
#include <iostream>
#include <cstdlib>
#include <cstring>
using std::cout;
using std::endl;
class Student
{
public:
Student(const char* name,const int& id)
:_name(new char[strlen(name) + 1]())
,_id(id)
{
strcpy(_name,name);
cout<<"Have done create"<<endl;
}
void release()
{
delete[] _name;
_name = nullptr;
}
void print() const
{
cout << "name:" << _name << endl;
cout << "id:" << _id << endl;
}
void* operator new(size_t sz)
{
malloc(sz);
cout<<"Operator new"<<endl;
}
void operator delete(void *p)
{
delete p;
cout<<"Operator delete"<<endl;
}
private:
char* _name;
int _id;
~Student()
{
if(_name) release();
cout<<"~Student"<<endl;
}
};
void test2()
{
Student* sp1 = new Student("Jackie",101);
sp1->print();
sp1->delete;
}
int main()
{
test2();
return 0;
}
|
此时我们运行发现,在sp1->delete行出错,由此我们知道delete在销毁对象时调用了析构函数,而析构函数因为他的私有化而不可用,因此需要在public里新建一个函数用来替换delete操作
void destroy()
{
this->~Student();
}
|
此时我们在内存检测时发现,对象本身没有被真正销毁,因此在destroy内部调用析构函数是错误的,应该直接进行delete操作,由于是在类的内部进行delete,可以访问析构函数,所以其操作是完全可行的
void destroy()
{
delete this;
}
|
代码实现
#include <iostream>
#include <cstring>
using std::cout;
using std::endl;
class Student {
public:
Student(const char* name, const int& id)
:_name(new char[strlen(name) + 1]())
, _id(id)
{
strcpy(_name, name);
cout << "Have done create!" << endl;
}
void release()
{
delete[] _name;
_name = nullptr;
}
void destroy()
{
delete this;
}
void print() const
{
cout << "name:" << _name << endl;
cout << "id:" << _id << endl;
}
void* operator new(size_t sz)
{
cout << "Operator new" << endl;
return malloc(sz);
}
void operator delete(void* p)
{
cout << "Operator delete" << endl;
free(p);
}
private:
char* _name;
int _id;
~Student()
{
if (_name) release();
cout << "Have done delete" << endl;
}
};
void test2()
{
Student* sp1 = new Student("Jackie", 100);
sp1->print();
sp1->destroy();
}
int main()
{
test2();
return 0;
}
|
打印结果
Operator new
Have done create!
name:Jackie
id:100
Have done delete
Operator delete
|








